Word to Describe a Molecule With an Unequal Charge Distribution
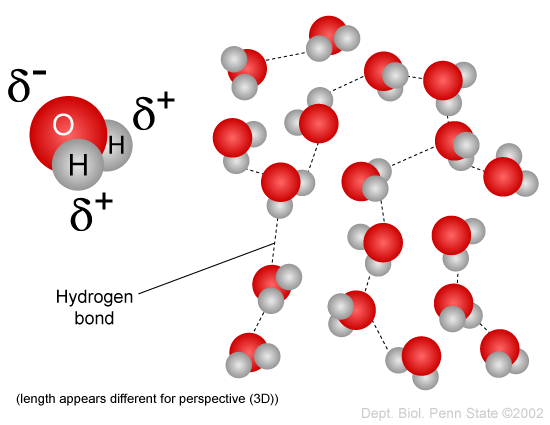
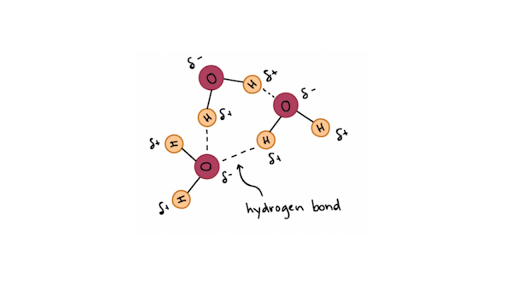
Bonding that is responsible for the relatively high boiling point of water. Hydrogen Bond Weak chemical bond formed by attraction of positively charged hydrogen atoms to other negatively charged atoms.

How Do Geckos Stick To Walls Intermolecular Force Chemistry Infographic
A molecule having two such charges or poles.

. Crossword Puzzle Across. Both mass and charge. Word used to describe a molecule with an unequal charge distribution.
Type of covalent bond in which one atom donates both electrons. What is a word used to describe a molecule with an unequal charge distribution. A representation in which we describe the electron structure of a molecule having delocalized bonding by writing all possible electron-dot formulas Triple bond a covalent bond in which three pairs of electrons are shared by two atoms Valence electron an electron in an atom outside the noble gas or pseudo-noble-gas core Lewis Dot Notation.
The atoms in a molecule of hydrogen chloride are held together by. Which type of bonding is found in all molecular substances. Word to describe a molecule with an unequal charge distribution.
Type of covalent bond found in diatomic molecules Nonpolar. Particles formed from covalent bonding. Because of this structure water is said to be.
The simultaneous attraction of electrons for a nucleii of two or more atoms is a chemical. Word to describe a molecule with an unequal charge distribution. The simultaneous attraction of electrons for the nuclei of two or more atoms is a chemical ______________.
What is a word to describe a molecule with an unequal charge distribution is polarA polar is a molecule with an uneven distribution of charge due to unequal sharing of electrons during bondingA. A molecule with an unequal distribution of charge which results in the molecule having a positive end and a negative end is called a polar molecule. A molecule that is polar.
What is a type of bond formed between an active metal and a nonmetal. A pair of electric charges or magnetic poles of equal magnitude but of opposite sign or polarity separated by a small distance. When a molecules atom has an unequal distribution of electrons in the orbitals it becomes polar as it carries an unequal charge.
Type of covalent bond in which one atom donates both electrons. Ammonia is polar because its shape is. 2 the intermolecular attractions resulting from the constant motion of electrons and the creation of instantaneous dipoles.
An antenna consisting of two rods of equal length extending outward in a straight line. Word to describe a molecule with an unequal charge distribution. Type of bond formed between an active metal and a nonmetal.
Resulting in a balanced distribution of electrical charge. A molecule with an unequal distribution of charge resulting in a positive end and a negative end. Can form a hydrogen bond.
Type of bond formed between a metal and nonmetal. Type of bond formed between an active metal and a nonmental. What is the simultaneous attraction of electrons for the nuclei of two or more atoms.
The total number of electrons in a neutral atom equals the number of. Word to describe a molecule with an unequal charge distribution. Protons in its nucleus.
The water molecule has two distinct ends each with a partial electrical charge. Has an unequal charge. The simultaneous attraction of electrons for a nucleii of two or more atoms is a chemical.
Type of bond formed between an active metal and a nonmental.

Hot Articles Chemical Communications Blog

Chemistry Ii Water And Organic Molecules

Heterogeneous Compounds Clue Chemistry Life The Universe And Everything
Molecules And Compounds Overview Atomic Structure Article Khan Academy

Polar Vs Non Polar Bonds Molecules Chemtalk

Microscopic Study Of Molecular Double Doping The Journal Of Physical Chemistry A
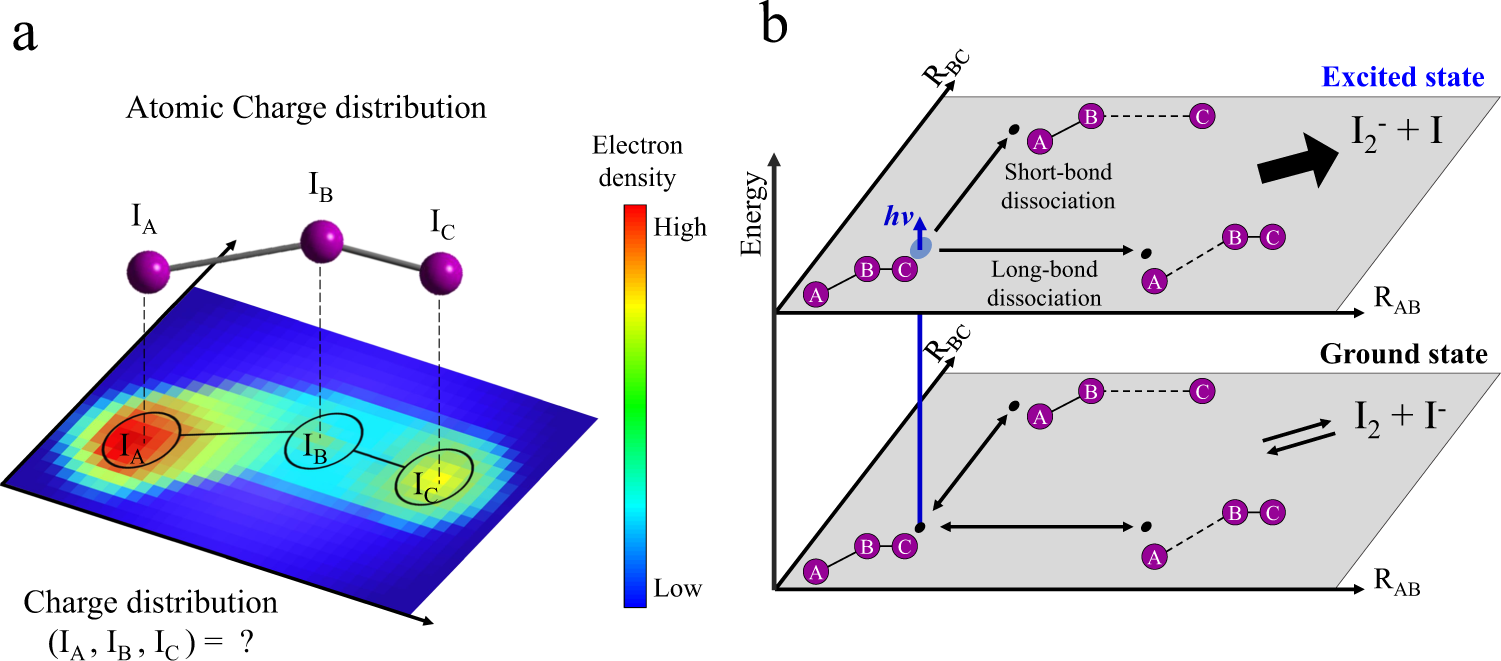
Determining The Charge Distribution And The Direction Of Bond Cleavage With Femtosecond Anisotropic X Ray Liquidography Nature Communications
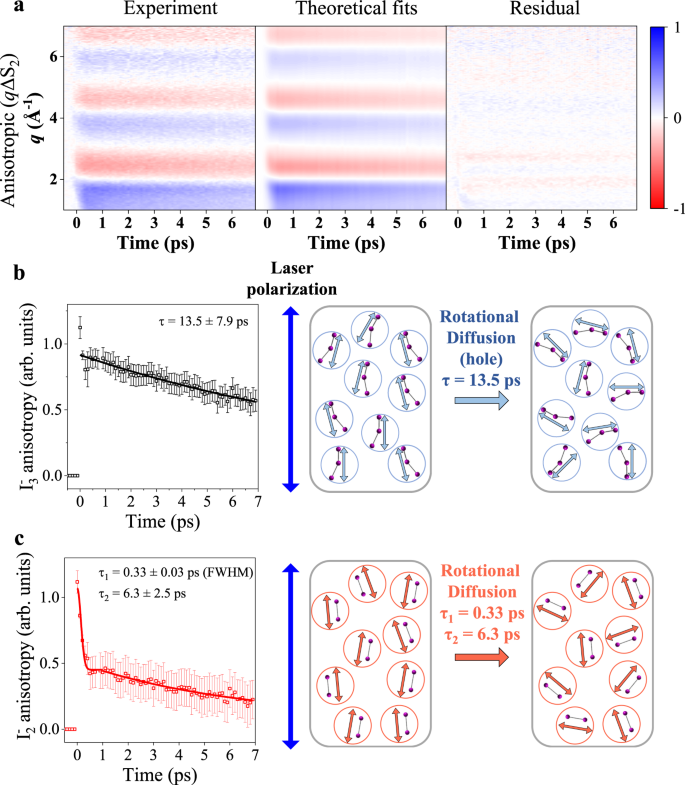
Determining The Charge Distribution And The Direction Of Bond Cleavage With Femtosecond Anisotropic X Ray Liquidography Nature Communications
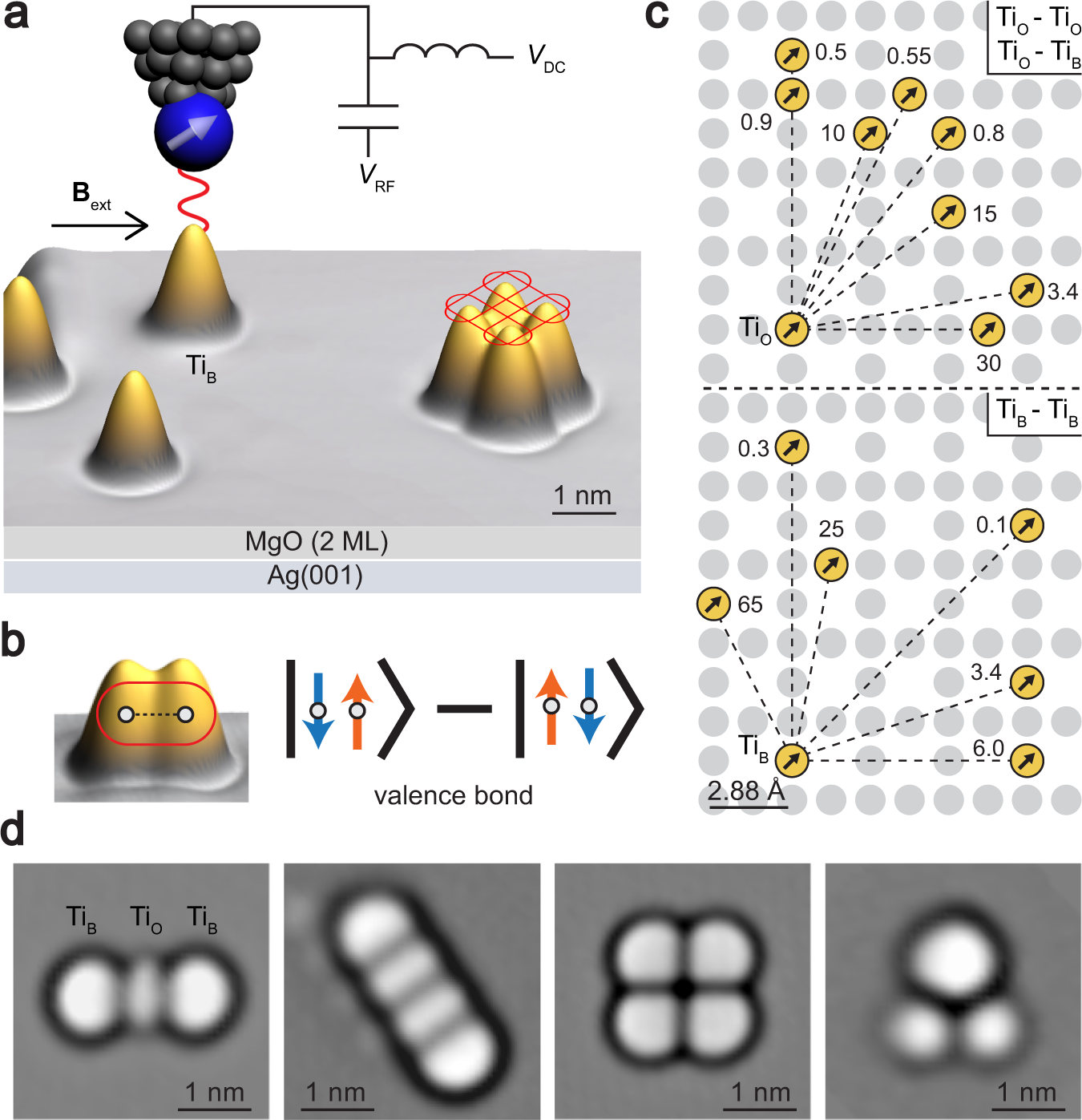
Probing Resonating Valence Bond States In Artificial Quantum Magnets Nature Communications

Composition Genes In Materials
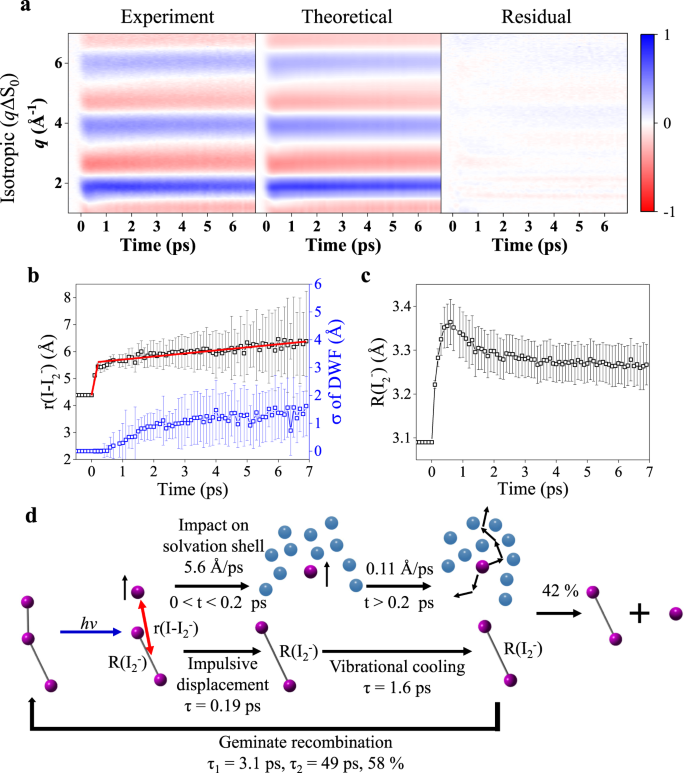
Determining The Charge Distribution And The Direction Of Bond Cleavage With Femtosecond Anisotropic X Ray Liquidography Nature Communications
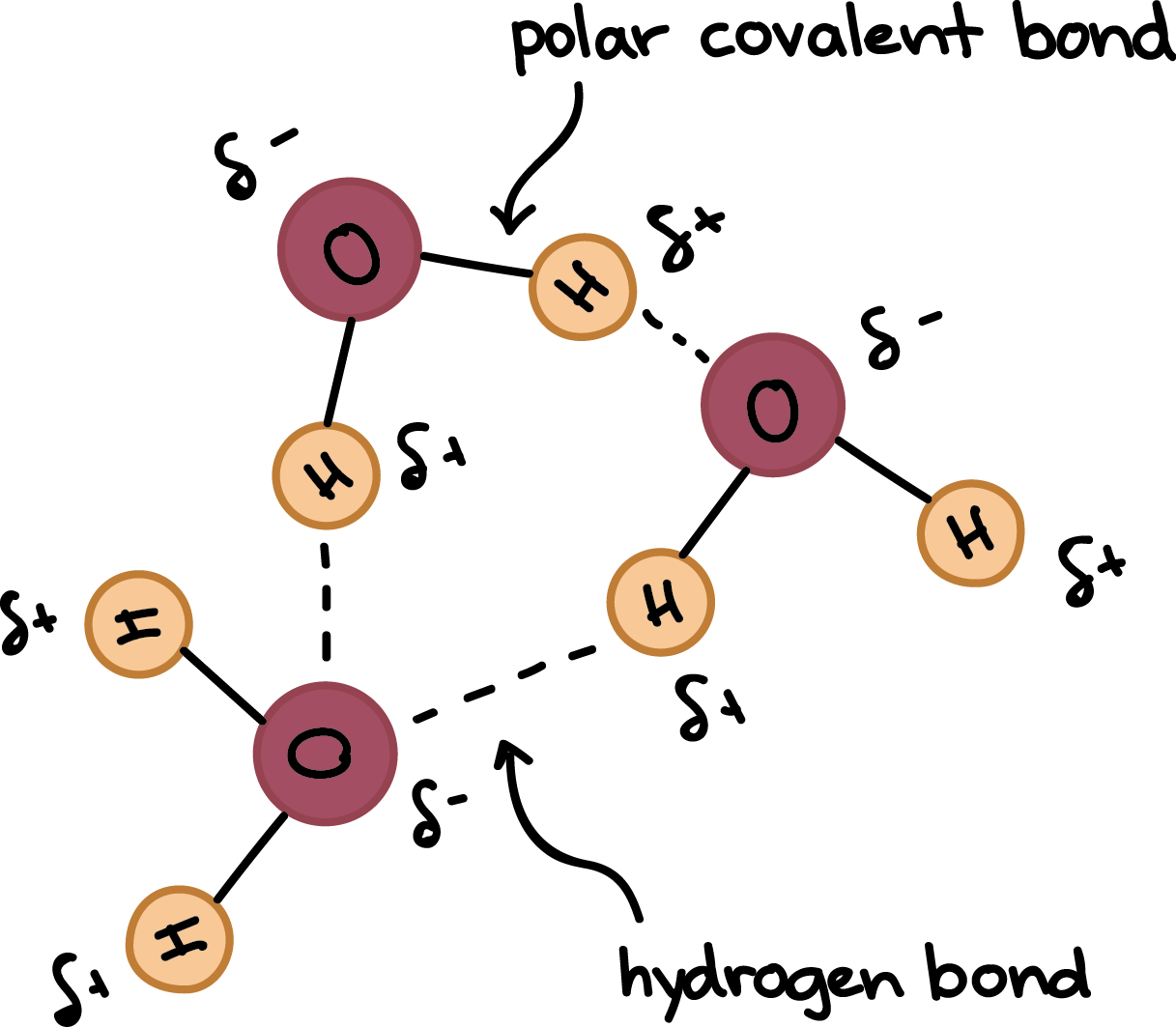
Hydrogen Bonds In Water Article Khan Academy

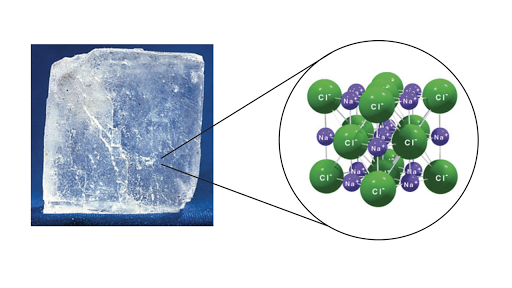
Crystal Types Of Bonds Britannica

Polar Vs Non Polar Bonds Molecules Chemtalk
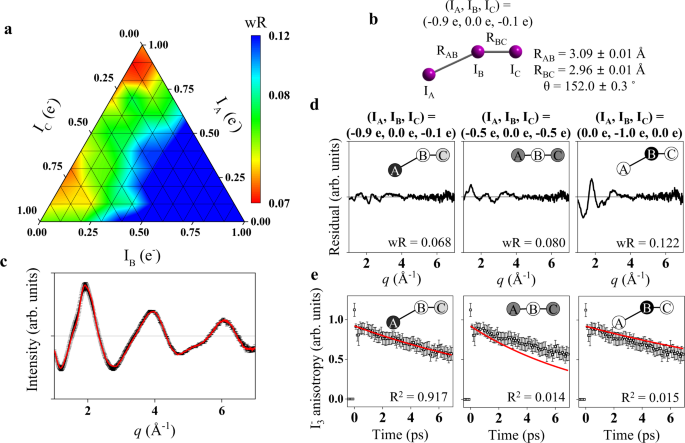
Determining The Charge Distribution And The Direction Of Bond Cleavage With Femtosecond Anisotropic X Ray Liquidography Nature Communications

Molecules And Compounds Overview Atomic Structure Article Khan Academy